Understanding O-RAN: Architecture, Interfaces, Algorithms, Security, and Research Challenges
Section II key principles of the O-RAN architecture, its components, control loops
Section III near-real-time RIC, RAN control
Section IV non-real-time RIC
Section V O-RAN interfaces
Section VI (AI)/ML workflow supported in O-RAN networks.
Section VII summarizes the main O-RAN use cases and related research esults.
Section VIII reviews security challenges in O-RAN
Section IX development efforts and structure of the O-RAN Alliance.
Section X Publicly-available research and experimental platforms for O-RAN
Section XI future directions and challenges for the Open RAN
Section XII concludes
Interface
- E2, O1, A1, O-RAN FH
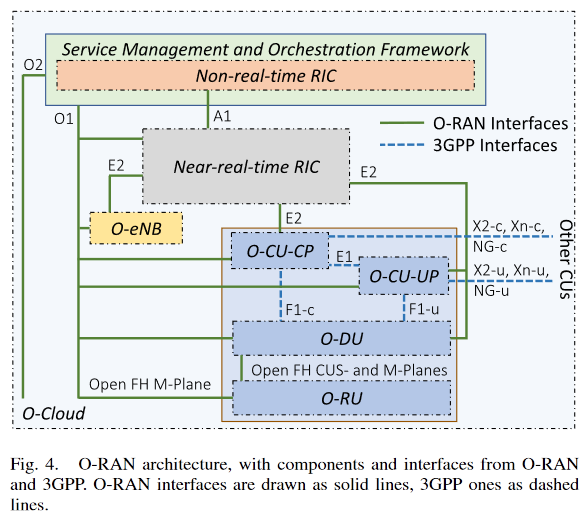
E2 interface
- E2 소개
- near-RT RIC과 E2Node(CU, DU, gNB) 연결
- 역할 1 : RIC이 RRM을 관리하도록
- 역할 2 : RIC이 E2Node의 기타 기능 제어을 관리하도록
- 역할 3 : RAN의 metric을 near-RT RIC으로 수집 (event trigger or period)
- 역할시 보조 도구 : 수집 시 사용되는 고유 식별자 (gNB, slice, QoS class, UEID)
- SCTP protocol 기반으로 작동 (UDP, TCP보다 발전된 방법이지만 기존 시스템과의 호환성 문제 때문에 잘 사용되진 않아왔음)
- E2 구성
- E2AP + E2SM
- E2AP
- E2 application protocol
- E2Node와 near-RT RIC 사이 통신의 기본 protocol
- E2AP message는 다양한 기능의 E2SM을 포함
- E2SM
- E2 service model
- E2AP
- E2AP + E2SM
- E2 할일
- 각각의 E2Node는 다양한 RAN function을 노출함
- RAN function 마다 출력하는 metric이 존재하며 이를 near-RT RIC의 xApp이 사용하고자 함
- near-RT RIC의 xApp은 원하는 metric을 출력하는 E2Node의 RAN function을 E2 interface, publish-subscribe mechanic을 통해 구독
- E2AP의 역할 at lowest level (with E2SM)
- interface management
- setup, reset, reporting of error
- near-RT RIC service update
- exchange of the list of the RAN functions
- procedure
- SCTP connection 생성 (near-RT RIC, E2Node)
- E2AP는 4가지 service를 제공
- 위의 service를 서로 다르게 조합하여 E2SM에 맞는 방법을 선택하여 대화함
- E2AP의 4가지 service
- E2 Report
- “E2 RIC Indication message” (E2 Node의 data를 포함)
- E2 Node가 자신의 function을 구독한 xApp에 data를 보내는 service
- 보내는 타이밍은 subscription 설정 도중에 period, event trigger일지 정함
- E2 Insert
- 긴급한 상황이나 중요한 변화가 생겼을 때 사용하는 service
- E2Node -> near-RT RIC의 xApp : 특정 event
- “RIC Indication message (of type insert)” 포함
- Insert message를 받은 xApp은 결정을 내리기 위해 잠시 정지 후 다음과 같이 행동
- response : timer를 중지하고 절차를 계속 진행함
- Timer expires, continue : timer가 끝나고, 절차를 계속 진행함
- Iimer expries, halt : timer가 끝나고, 절차를 종료함
- E2 Control
- RIC에 의해 자동으로 시작되는 service
- insert message에 대한 결과
- “RIC Control Request message” : RIC -> E2Node
- RAN function의 parameter에 영향을 미치라는 request를 할 수 도 있음
- “RIC Control Acknowledge” : RIC <- E2Node
- E2 Policy
- subscriptpion procedcure를 어떻게 진행할 것인가에 대한 service
- event trigger
- policy (E2 node가 자율적으로 따라가야하는 rrm 정책)
- E2 Report
- 4가지 service들을 이용하여
- 위의 4가지 service들은 service model(E2SM) 생성하기 위해 결합
- E2AP message의 일부로 삽입
- ASN.1 notation을 통해 encoding됨 (key-value function)
- interface management
- E2 Service Models
- O-RAN Allicance WG3에서 4가지 service model을 소개
- E2SM KPM
- E2SM Network Interface(NI)
- E2SM Cell Configuration and Control(CCC)
- E2SM RAN Control(RC)
- E2SM KPM
- RAN으로부터 performance metrics가 report
- E2 report service 사용
- procedure example (E2 Setup)
- E2 node가 자신의 metric을 광고
- xApp이 E2 node에 subscription message를 보냄
- message : 필요한 KPM, trigger/period
- E2Node가 report type의 indication message를 사용해 해당 KPM을 stream
- E2SM Network Interface(NI)
- 다양한 network interface에서 E2Node가 받은 message를 이용
-
message를 E2 interface를 통해 near-RT RIC으로 report message를 생성하는데 이용
- 이 때 E2Node는 자신이 어떤 network interface를 지원하는지 expose함
- E2SM Cell Configuration and Control(CCC)
- cell/node 수준에서 E2Node의 control + configuration
- E2 report service와 E2 control service 사용
- ex) 다음과 같은 값을 control
- X2 and Xn neighbors
- RAN slicing
- bandwidth part
- ynchronization signals of a cell.
- E2SM RAN Control(RC)
- E2Node의 RRM를 최적화
- E2 control service 사용
- CCC보다 더 세밀한 control을 목표로 (ex> UE 식별 기능/ UE 정보 report)
- RC의 종류
- radio bearer control
- radio bearer : network에서 data를 전송하는 경로
- QoS parameter, bearer admission contro, split bearer, PDCP duplication control
- radio resource allocation control
- slice 수준의 PRB을 위한 조정
- connected mode mobility control
- RRC 연결 상태에 있는 UE의 mobility procedure 시작 (HO)
- radio access control
- random access backoff를 위한 parametor set 설정
- UE의 cell 할당 등
- Dual connectivity (DC) control
- secondary cell로 UE를 HO 구성 및 trigger
- Carrirer Aggrecation (CA) control
- CA 시작, UE의 sub carrier를 수정
- idle mobility control
- RRC 연결이 안된 UE의 mobility procedure 수정 (cell 재선택, idle timer)
- radio bearer control
- 이들은 3GPP에서 정의된 information element(IE) 값을 사용
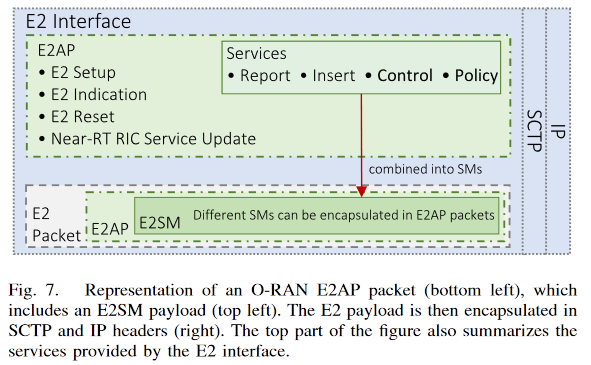
O1 interface
- O1 소개
- O-RAN management elements (near-RT RIC, RAN nodes)
- SMO, non-RT RIC
- 위의 둘 사이를 잇는 interface
- operation과 maintanance를 위한 standardized practice를 확장시긴 open interface
- O1 역할 1 : MnS를 지원
- Mangement Services (MnS)
- manamgent of the life-cycle of O-RAN components
- startup, configuration, falut tolerance, heartbeat service
- performance assurance
- KPI reports
- software and file management
- manamgent of the life-cycle of O-RAN components
- Mangement Services (MnS)
- MnS 1 : Provisioning Management Service
- SMO가 관리하는 노드에 configuration을 전달하게 함
- 외부 configuraiton update를 SMO에 report함
- 이를 위해 O1은 REST/HTTPS API, NETCONF를 결합하여 사용함
- NETCONF
- Network function의 life cycle을 위해 사용
- IETF standard protocol (Internet Engineering Task Force)
- NETCONF
- MnS 2 : Fault Supervision MnS
- SMO에 falut, event에 보고
- falut는 3GPP에서 정의된 것을 기반
- RAN node가 REST API를 사용하여 표준화된 JSON paylod를 통해 falut를 report
- MnS 3 : Heartbeat Mns
- 관리하는 device에 heartbeat를 설정, VNF, PNF 관리
- heartbeat message : service, node의 상태와 가용성을 monitoring,
- 네트워크에서 특정 장치나 노드가 정상적으로 작동하고 있는지 주기적으로 확인
- MnS 4 : Performance Assurance MnS
- 성능 data을 SMO에 보고 (streaming or file report(일괄로))
- streaming
- handshake 이후 WebSocket이 사용됨
- file report, 일괄전송
- HTTP API, file 준비 alarm, MnS provier(RAN node) -> SMO
- SFTP를 통해 file 전송
- streaming
- 이를 통해 SMO가 data 분석, AI/ML을 위한 dtat collection 가능
- 이 때 SMO가 data 받을 KPI, 주기 선택 가능함
- KPI는 3GPP별, vendor별, WG별로 다름
- 성능 data을 SMO에 보고 (streaming or file report(일괄로))
- MnS 5 : Trace MnS
- SMO는 monitor trace-based events를 기반으로 다음의 event를 monitoring 할 수 있음
- profile calls, RRC connection establishement, radio link failures
- SMO가 관리하는 node에 file을 푸시하고 다운로드하는데 사용
- software update
- RU를 위한 beamforming configuration file
- ML model 및 보안 인증서 배포
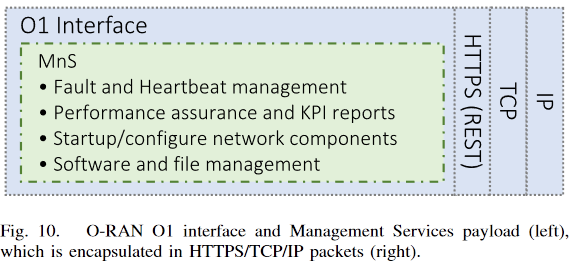
A1 interface
- A1 소개
-
non-RT RIC과 near-RT RIC을 연결하는 interface
- 역할 : Policy management
- non-RT RIC -> near-RT RIC : 정책 기반의 가이드 전달
- near-RT RIC : 가이드를 확인하고 적절한 조치
- 가이드 라인 내용
- 고수준 최적화 목표 설정
- ML model management
- near-RT RIC의 xApp에서 사용되는 ML model을 관리
- Enrichment Informantion
- near-RT RIC을 위한 enrichment information 전달을 negotiate, orchestrate (어떤 정보를 어떻게 보낼지를 관리)
- 이를 통해 near-RT RIC은 non-RT RIC에게 조건에 맞춰 해당 정보를 전달
- 가이드 라인 형식 : JSON schema
-
- A1AP application protocol
- 정책 배포 : 3GPP framework를 기반으로 함
- JSON 객체의 전송을 위해 HTTP를 통한 REST API를 사용
- REST API : 인터넷에서 데이터를 주고 받을 때 흔히 사용되는 방식
- non과 near은 모두 server 혹은 client 역할을 HTTP를 통해 함
- server는 데이터를 제공하고, client를 데이터를 요청
- 역할 1 : Policy management
- non-RT RIC이 RAN의 intent를 달성하기 위해 policy 정의
- intent : UE, slice의 QoS와 KPI를 통해 정의되며, 이 값들은 O1, A1를 통한 report 기능을 통해 monitoring됨. (O1 interface를 통해 SMO(non-RT RIC)에 data report 되니까)
- 생성된 policy는 A1을 통해 near-RT RIC에 전달되어 xApp을 통해 구현.
- policy의 life-cycle은 non-RT RIC이 담당하여 모니터링하고 관리
- non-RT RIC이 RAN의 intent를 달성하기 위해 policy 정의
- about Policy
- JOSN schema를 기반
- 구성 : policy identifier + scope identifier + 1개 이상의 policy statement
- policy identifier : non-RT RIC의 고유한 정책 식별자
- scope identifier : 단일 UE, UE group, sclice, cell, bearer, application classes
- policy statement : policy resource(자원 사용 조건) + policy objectives(QoS,KPI 측면의 목표)
- 역할 2 : Enrichment Information (EI)
- 일반적으로 RAN 자체에서 사용할 수 없는 정보를 제공하여 RAN 성능을 향상 시킴
- capacity forecasts, information elements from sources outside the RAN, aggregate analytics
- SMO와 non-RT RIC이 외부 정보에 접근하여 얻은 정보들을 A1을 통해 near-RT RIC의 xAPP에 전달
- A1을 통해 정보 source와 xApp을 직접 연결할 수도 있음
- 일반적으로 RAN 자체에서 사용할 수 없는 정보를 제공하여 RAN 성능을 향상 시킴
O-RAN fronthaul interface
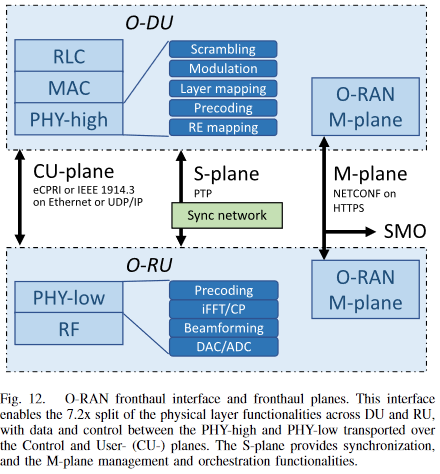
- 소개
- DU - RU (다수)
- 역할
- RU의 physical layer 기능을 분배
- DU에서 RU 작업을 제어
- split 7.2x (O-RAN alliance가 3GPP에서 제안한 split 중 해당 split을 사용)
- physical layer 기능을 RU와 DU로 나누어 수행
-
각 장비의 처리 능력에 따라 최적화할 수 있도록 해줌 (복잡한건 DU)
- RU - 물리계층의 하부가 RU에 존재 - DL : OFDM 위상 보상, reverse FFT, CP 삽입 -> 주파수를 시간으로 변환 - UL : FFT, CP 제거 - RU에 능력에 따라 기능이 추가되거나 제거될 수 있음 - DU - scrambling, modulation, layer mapping, RB mapping
- 7.2x split
- trade-off (장점만 소개한 듯)
- interface의 단순성과 RU 설계
- interface와 RU가 상대적으로 간단하여 구현이 용이, 유지보수 편함
- 상호 운용 가능성
- phy layer를 너무 많이 분할하면 설정 매개변수가 많아져 다른 장비와 호환성 떨어짐
- 7.2x split은 설정할 매개변수가 적어 다른 장비화 호환성이 좋음
- fronthaul에 필요한 데이터 전송 속도
- phy layer를 덜 분할하여 전송해야할 데이터 양이 적어 높은 전송속도를 요구하지 않음
- interface의 단순성과 RU 설계
- fronthaul data transmit
- Ethernet or UPD/IP encapsulation
- eCPRI와 같은 payload 전달 가능 (RU와 DU의 통신을 정의하는 데 사용되는 interface)
- DU와 RU
- DU는 여러 개의 RU를 지원
- 1개 cell의 data를 여러 개의 RU로 나누어 보낼 수 있음
- 여러 cell의 data를 1DU-nRU를 통해 처리할 수 있음
- DU는 여러 개의 RU를 지원
- 해당 interface는 DU-CU간 저지연을 지원하도록 설계
- 네트워크 부하를 줄이기 위한 다양한 modulation compression 기술 등을 지님
- trade-off (장점만 소개한 듯)
- 4가지 function(plane)
- U(user plane) : 데이터 전송
- C(contorl plane) : phy layer control message 전송
- S(synchronization plane) : DU-CU 간의 타이밍 관리
- M(management plane) : DU 자체에서 RU 기능 구성을 관리
- C-plane
- DU의 high-PHY -> RU의 low-PHY
- 명령 전달 : scheduling, beamforming, NR numerologies, DL precoding, spectrum sharing control
- C-plane의 command -> U-plane의 packet에 결합되는 방법
- eCRPI, IEE 1914.3 header와 paylod에 encapsulation 되어 전달
- C-plane과 M-plane의 결합
- RU의 beamforming 기능을 구성하고 관리하는데 사용
- 진폭, 위상, digital precoding weights를 선택할 수 있는 4가지 beamforming 옵션 지원
- predefined-beam beamforming
- attributed-based beamforming
- weight-based beamforming
- channel-information-based beamforming
- 값들 선택은 DU가 함
- 진폭, 위상, digital precoding weights를 선택할 수 있는 4가지 beamforming 옵션 지원
- RU antenna의 model은 안테나 요소, 편광, 패널 위치 및 방향을 정의함으로써 DU가 식별 잘함
- RU의 beamforming 기능을 구성하고 관리하는데 사용
- U-plane
- RU와 DU 간의 주파주 domain에서 I/Q(복소수) sample을 전송
- C-plane message가 전송되면 U-plane에서는 I/Q sample이 1개 이상 포함된 message로 이어짐
- S-plane
- DU, RU의 시계 간의 시간, 주파수, 위상 동기화를 담당
- data channel, control channel의 전송 및 수신을 위한 resource를 적절하게 정렬할 수 있음
- M-plane
- DU-RU에 있는 전용 endpoint가 IPv4 or IPv6 터널을 설정하여 C-, U-, S- plane과 병렬로 실행되는 protocol
-
SSH 및 TLS를 통해 종단 간 암호화
- 역할 1 : DU, RU 간의 연결 초기화 및 관리, RU의 구성을 담당
- 구조 1 : SMO -> DU -> RU
- 구조 2 : SMO -> RU (O1 interface)
- 역할 2 : RU의 life-cycle 관련 업무 담당
- DU or SMO와 연결 설정 시작 단계 관리
- software update, configuration, performance, fault monitoring 등
- RU 등록, RU-DU 간 매개변수, beamforming vector updte 등
Other Interface
- O2 interface
- SMO와 O-RAN, O-Cloud를 연결
- 네트워크 기능의 관리 및 provisioning을 programming 방식으로 가능하게 함.
- O-Cloud에서 제어하는 시설의 inventory 정의, monitoring, provisioning, 내결함성 및 업데이트를 허용
- E1 Interface
- CU 제어와 user function을 연결
- F1 Interface
- CU와 DU 연결
- user, control plane을 위한 전용 sub interface를 통해 연결함
- Xn (X2) Interface
- gNB끼리 연결
- Uu Interface
- UE와 gNB를 연결
- NG Interface
- gNB를 5GC의 UPF와 AMF에 연결
- UPF(user plane을 위한 user plane function)
- AMF(control plane을 위한 access and mobility management function)
about Cloud-RAN chain
- 자원 검색(Resource Discovery)
- computing 자원 : 대상 커버리지 영역 근처에서 computing 자원을 자동으로 검색
- 안테나 위치 : 물리적 안테나가 위치한 장소와 근접한 네트워크 자원을 검색
- 최적 배치 결정(Optimal Placement Decision)
- latency 고려 : 검색된 자원을 바탕으로, 초저지연을 위해 RU, DU, CU 유닛의 최적 배치를 결정
- 전송 거리 최적화: RU와 DU 간의 프론트홀 전송 거리(지연 시간)를 최소화하여 중앙 집중화의 이점을 최대화
- 자동 구성(Automated Configuration)
- 동기화 : 발견된 자원을 사용하여 RU, DU, CU 유닛 간의 동기화를 설정
- 자동화된 설정 : 각 유닛을 자동으로 설정
- 서비스 시작(Service Initialization)
- 네트워크 서비스 시작 : 구성된 Cloud-RAN 체인을 기반으로 네트워크 서비스를 자동 시작
- 상위 오케스트레이션 통합 : 상위 오케스트레이션 계층에서 API를 통해 이 모든 과정을 시작하고 관리할 수 있습니다.
- 모니터링 및 관리(Monitoring and Management)
- NMS 통합: 전용 네트워크 관리 시스템(NMS)을 통해 생성된 인스턴스들을 모니터링하고 관리합니다.
- 그래픽 인터페이스: 그래픽 사용자 인터페이스를 통해 네트워크의 상태를 확인하고 필요한 조치를 취할 수 있습니다.