NeutRAN: An Open RAN Neutral Host Architecture for Zero-Touch RAN and Spectrum Sharing
abstract
- 전통적 문제점
- network operator의 capital expense (exclusive spectrum, cell sites, RAN equipment, edge infra)
- 해결책
- neutral host infrastructure을 통해 expense를 줄일 수 있음
- network operator에게 RAN service를 제공 (virtualization, slicing)
- neutral host infrastructure을 통해 expense를 줄일 수 있음
- 해결책의 문제점
- 그러나 현재 존재하는 neutral host : lack automated, virtualized pipelines
- 새로운 해결책 : NeutRAN
- zero-touch framework based on the O-RAN architecture
- optimization engine : 제한된 specturm과 RAN node를 이용해 coverage와 quality를 보장
- micro-service : optimization engine을 가상화, 자동화하기 위해
- simulation 구성
- 4 OpenShift cluster + programmable testbed (3tenant, 각 10user)
- simulation 결과
- 10초 만에 neutral host based cellular network 배포
- 사용 주파수 : 30MHz 공유 spectrum
- cumulative network throughput 2.18배 증가
- per-user average throughput 1.73배 증가
- 사용 주파수 : 10MHz 공유 spectrum
- cumulative network throughput 1.77배 증가
introduction
-
network 발달로 인한 expense 증가
- neutral host infrastructure의 소개 및 역할
- 비용절감
- infra 공유
- spectrum 공유
- neutral host infrastructure의 문제점
- fine-grained sharing의 부재
- 동일한 infra에서 computing과 spectrum slicing 세분화해서 tenant들이 공유하는 메커니즘이 부족
- dynamic sharing
- spectrum을 공유할 때 시스템이 적응하고 조정하는데 시간이 걸리는 것이 문제
- 필요에 따라 주파수와 infra를 즉시 공유하고 조정할 수 있어야하는데 그렇지 못함
- Lack of automated and virtualized pipelines for multi-tenant management
- 이게 있어야 여러 회사가 문제 없이 infra와 spectrum을 공유할 수 있음.
- Lack of timely management of the life cycle of network services
- 복잡한 소프트웨어 서비스(소프트웨어화된gNB)가 빠르게 instance화되어야 하기 때문에, spectrum 및 RAN infra 리소스의 dynamic allocation이 어렵
- 저지연 종단 간 파이프라인이 부족하기 때문 (RAN, resource, interface 관리를 통해 network service의 life cycle을 관리하는 pipeline)
- Operators’ perception of resource sharing as a risk
- 운영자는 exlusive spectrum 라이센스를 선호
- dynamic, fine-grained 리소스 할당을 통해 SLA 지원할 수 있는 공유 solution이 없기 때문
- tenant requests, available resources, and network analytics to generate an optimal allocation of micro-services and spectrum resources (e.g., spectrum slices)
- fine-grained sharing의 부재
- NeutRAN
- zero-touch dynammic and fine-grained RAN and spectrum sharing
- tenant로부터의 high-level intents와 request를 만족
- 다음 2가지를 포함한 end-to-end pipeline을 통해 구현할 수 있음
- virtualized, automated RAN infrastructure
- optimization engine with sarhing policies
- Contribution
- NeutRAN zero-touch framework and automation pipelines
- OpenShift, Kubernetes, O-RAN, SDR을 이용해 prototype을 구성
- centralized SMO -> edge datacenter, cell site로 9초만에 네트워크 구성 가능
- RIC, xApp, rApp도 배포
- NeutRAN optimization engine rApp
- latency와 QoS, SLA를 보장하는 engine
- neutral host problem 모델 : binary QCQP optimization problem
- (Quadratically Constrained Quadratic Programming)
- 최적화 방법 : reformulation linearization techniques
- rApp : O-RAN interface로 RAN 성능에 대한 data 및 분석을 수집
- rApp은 SMO에서 관리, 배포가 이루어짐
- calability, efficiency, and experimental evaluation
- 대규모 네트워크 구성 -> 최적 solution 계산 -> tenant의 요구사항 만족하는 resource를 할당
- simulation
- 환경 : 기지국 4개, 3개 tenant (UE 10개씩), RAN(10MHz, 30MHz)
- 결과
- 30MHz : RAN 처리량 2.18배, 평균 사용자 처리량 1.73배의 증가, SINR 일관되게 개선
- 10MHz : RAN 처리량 1.77배의 개선, 평균 사용자 처리량은 유지 (스펙트럼이 감소됐음에도 성능이 감소하지않음을 말하고싶은 듯)
- NeutRAN zero-touch framework and automation pipelines
NeutRAN Framework
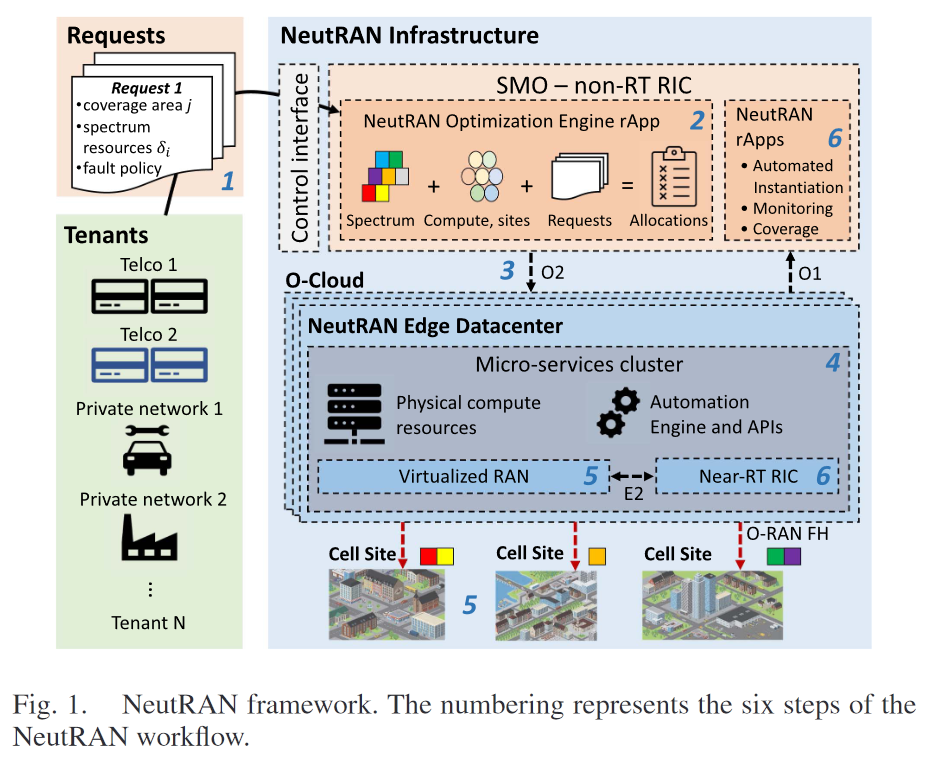
- NeutRAN = infra + engine
- infra : O-RAN 기반 소프트웨어화된 자동 infra
- engine : 효율적인 RAN, spectrum 공유를 위한 최적화 engine
- NeutRAN 이해관계자 = tenent, operator
- tenent : 최종 사용자에게 서비스를 제공
- operator : infra 소유, 자동화된 RAN, spectrum 공유 pipeline에 접근을 제공
O-RAN
- O-RAN
- cloud native 원칙을 기반으로 구축된 mobile cellular network를 배포하기 위한 분산 접근 방식
- 구성요소
- 분산된 network 요소 : CU, DU, RU, RIC
- 표준화된 interface (구성 요소 간의 상호 운용성 촉진)
- RIC
- 데이터 기반의 closed-loop control 및 network management application(xApp, rApp)을 이용
- non-RT RIC(비실시간), near-RT RIC(실시간)
- app들이 RAN에서 실시간으로 KPM을 수신하여 동적 채널 조건과 트래픽 수요에 맞게 configuration을 조정함
- O-cloud
- O-RAN이 O-Cloud의 computing resource pool에서 RAN을 위한 가상 service를 배포함
- cloud에 배포된 SMO에 의해 관리됨 (SMO가 service를 관리한다는 말이겠지)
- SMO
- O-RAN의 O1 interface를 사용 : 네트워크 infra, resource (computing, spectrum, coverage)의 추상적인 view를 제공
- O-RAN의 O2 interface를 사용 : O-Cloud의 가상화 자원에 연결하여 새로운 service 배포 및 update를 트리거
- O-RAN의 non-RT RIC과 rApp이 실행되는 장소임
- SMO
NeutRAN 구성요소
- SMO
- optimization engine을 구현하는 rApp의 non-RT RIC instance로 구성
- rApp의 입력 : tenant request + monitoring rApp이 수집한 RAN의 분석 data
- tenant request : O-Cloud에 배포될 service에 matching
- optimization rApp 종류
- service instance화의 자동화를 맡는 rApp
- self-healing을 위한 infra monitoring을 맡는 rApp
- coverage rApp : 각 cell site가 커버하는 영역을 식별하기 위해 과거+현재 coverage data를 monitoring
- edge datacenter
- OpenShift를 통해 pipeline 구현
- redhat에서 제공하는 open source platform
- O-cloud 위에서 application을 쉽고 효율적으로 관리, 배포
- kubernets 기반으로 application, workload를 instance화(pod를 이용해 containerized virtualization)
- workload
- virtualized core network
- RAN (+ tenant별로 다른 CU, DU)
- near-RT RIC (+xApp)
- E2 interface 사용
-
xApp : 사용자 수요와 자원 사용을 예측하고 모니터링 -> engine 도움
<OpenShift pipeline + optimization engine rApp>을 통해 효율적인 datacenter resource를 sclicing할 수 있음
- OpenShift를 통해 pipeline 구현
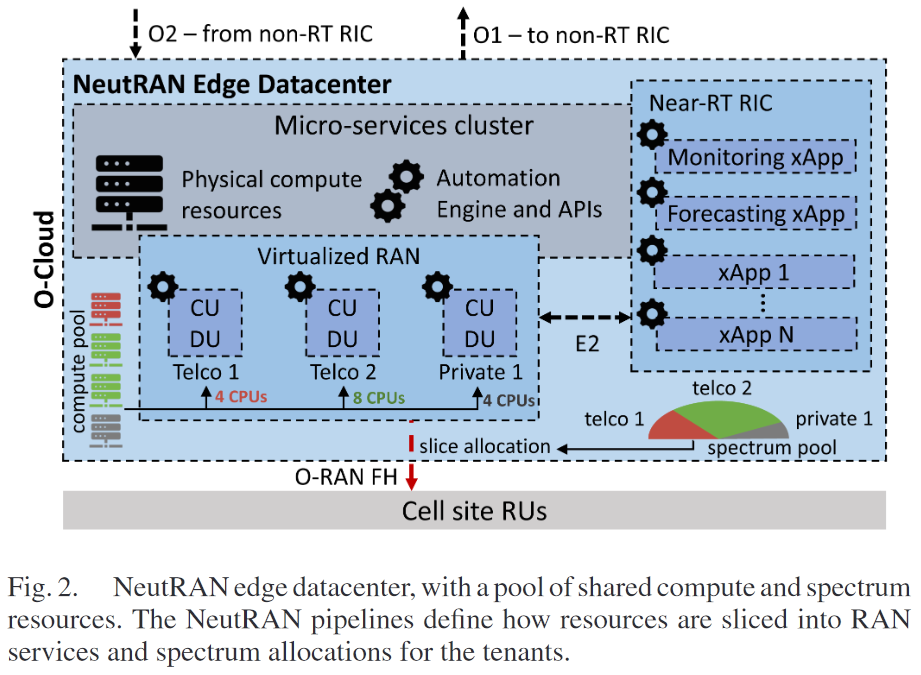
- cell site
- datacenter : O-RAN Fronthaul (FH) interface를 사용해 multiple cell site와 연결됨
- cell site에는 RU, antenna가 있음
NeutRAN 자동화 workflow
-
step 1 : tenant가 request를 NeutRAN에 제출
intent 종류 - 필요한 service - 필요한 resource - fault-recovery policies -
step 2 : SMO의 rApp(최적화 engine)에 input입력됨
- input : request + resource(spectrum, infra) -
step 3 : engine의 output인 policy가 edge datacenter에 전달
- output : resource allocation policy (O2 interface를 통해 datacenter에 전달) - resource allocation policy - 각 tenant에 할당된 spectrum(carrier freq, bw) - cell site - edge datacenter의 computing resource -
step 4 : edge datacenter에서 tenant가 요구하는 요소를 pipeline을 통해 준비, 실행
- tenant가 요구하는 것을 pipeline을 통해 instantiate - CU/DU - core network - near-RT RIC + xApp - instantiate가 끝나면 edge datacenter에서 RAN service가 실행됨 - core network와 near-RT RIC 연결 - RAN의 KPM이 RIC에 보고되어(by E2 interface) xApp이 사용 - 다수의 tenant가 동일한 기지국을 공유하는 상황이 생길 수 있음 (policy에 따라) -> 해결책 : tenant 별로 RAN sclicing을 사용 -> NeutRAN은 사용자에게 spectrum을 고정적으로 할당하나, sclicing xApp을 사용하여 동적으로 할당할 수 있음 -
step 5 : tenant가 요구하는 RAN, spectrum에 대한 microservice가 완전히 provision(instanciate)
-
step 6 : edge datacenter와 SMO의 monitoring
- 각각의 monitoring xApp, rApp을 실행하여 - resource를 monitoring - fault를 self-healing